
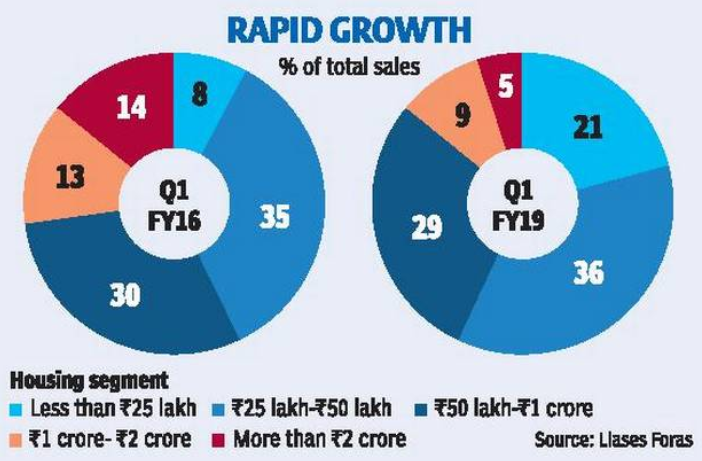
With the recent push by the government to promote low-cost housing in India and with a set target to build 20 mn affordable houses by March 2022, the affordable housing segment has seen a recent spurt in sales and demand. One in every five houses is now priced at less than INR 25 lakh. The total contribution of affordable housing to residential sales has increased to 21% from 8% within a span of 3 years. Between 2016 and 2019 sales have tripled for lost cost homes with year on year growth of 32% in Q2 2018.
As of February 2019, more than 16,000 project proposals have been considered with almost 8 million houses sanctioned in them and 1.5 houses amongst them already built and occupied. With such rapid strides in this segment, more and more popular technologies are being used to construct houses to not only reduce the time and cost of construction but also to build houses in a green, sustainable manner.
One of the most popular technologies currently in usage in India is the GFRG or Glass Fibre Reinforced Gypsum technology. GFRG panels are made up of high-density alpha-based gypsum plaster reinforced with glass fibres and were first introduced in Australia in 1980. This panel is eco-friendly, prefabricated and can be cut to desired sizes for walls, roofs with openings for doors and windows. In Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala, projects have already started by various developers with this technology to build houses, hospitals and schools.

Another technology which is hugely in demand in India is the Precast Modular Technology. The process involves the on-site assembly of standardized items that were manufactured in the factory and transported to the construction site. This technology involves the use of materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) panels, steel and fibre cement. This technology involves lesser cost and reduces construction time significantly. Companies like NCL Industries, Loom Crafts, Woodbarn India are offering pre-fabricated housing solutions. Globally, Burj Khalifa and Sydney Opera House are leading examples of this technology. With this technology, a house can be built in 2-3 hours, or a school in just 30 to 60 days. Meitra Hospital in Kerala is the first fully prefabricated hospital in India. Lulu Mall, in Lucknow, is being built with the pre-fabricated construction materials.


The last technology that needs to be discussed is the monolithic reinforced concrete construction system. This system is a popular and widely recognized as a practical and low-cost solution to effective housing on a mass scale. This system allows the contractor to cast foundations, walls, ceilings according to a pre-defined cycle. Recently, the Central Public Works Department has decided to adopt monolithic construction technology for all projects above INR 100 crore. This would ensure less manual intervention and elimination of entire plastering. Currently, this technology is being used in EWS housing projects in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha and Maharashtra.

New technologies are still in the emerging phase in India, with most of them under research in premier institutions like IITs and others under trial with BMTPC, NBCC etc. However, with the Government’s push towards affordable housing over the next 4 - 5 years, these technologies can sure provide the right balance between quality and cost, an issue that is being faced by developers in India.



