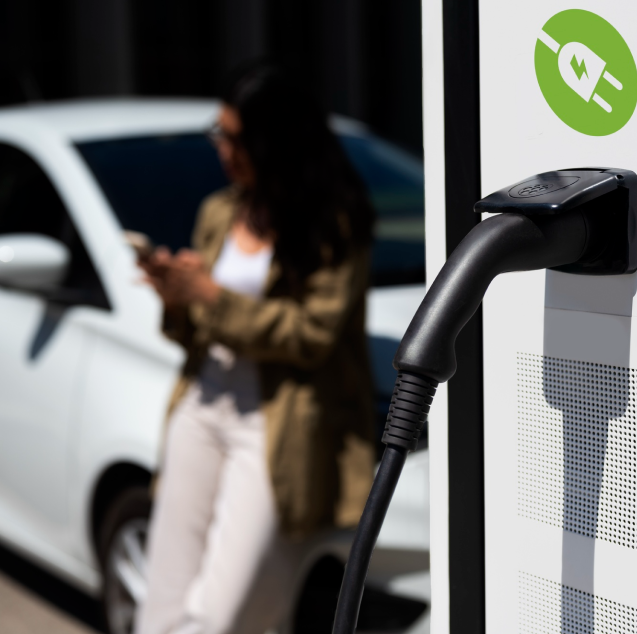
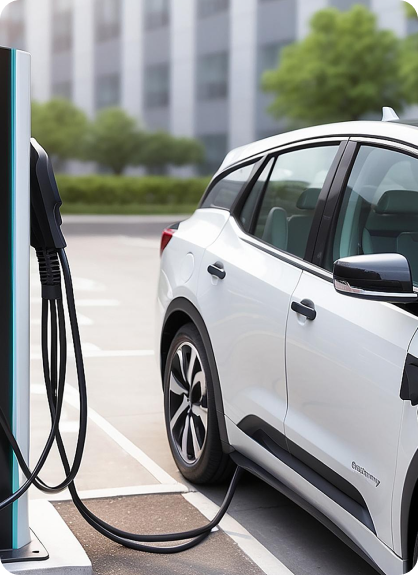
Why Invest in Electric Mobility
-
Large Market
India is the 3rd largest automotive market in the world in terms of sales, ahead of both Japan and Germany. A switch to electric vehicles, therefore, opens up potential for sales on a grand scale.
-
Reduced Tax Rates for EVs
GST Rate of 5% for EVs compared to 28% for conventional ICE vehicles
-
Incentives
India’s central and state governments have launched lucrative policies like Production Linked Incentives and FAME for companies to set up manufacturing plant and customers to adopt EVs and suppliers to push domestic production and network buildout.
-
Attractive Global Investments
In 2024, the government approved a new $ 500-million-worth EV Policy, offering a range of incentives with the intention of drawing investments from global EV companies and positioning India as a prime manufacturing hub for state-of-the-art EVs.